Data Scraping
Introduction :
Every data scientist requires data to perform their work. The process of collecting data can be challenging, especially when dealing with incompatible software or when a quick search for the required data is needed ,
sometime we deal about some source of information like Kaggle , Google dataset search ,UCI machine learning repository and more
- What would be a viable solution to streamline this data acquisition process?
One of the solution is to do data scraping, web scraping and data scraping or data parsing are often confused with each other, even though these two terms refer to distinct practices. In this dedicated article, we explore the true definition of web scraping and its various key stages: crawling, fetching, parsing, and storage.
Domain-Specific Data Collection:
Data scraping is employed across a wide range of domains to gather domain-specific datasets. Some common examples include:
1. E-commerce :
- Scraping product details, prices, and customer reviews from online marketplaces to analyze market trends, monitor competitors, or build recommendation systems.
2. Social Media:
- Extracting posts, comments, and user information from social media platforms for sentiment analysis, user behavior studies, or identifying trending topics.
3. Research :
- Collecting scientific papers, articles, and publications from academic websites to create datasets for research purposes.
4. Real Estate :
- Scraping property listings, prices, and location details to analyze real estate market trends, assess property values, or build property recommendation systems for example we can use it in marketing or e-reputation .
5. Finance:
- Retrieve financial data, stock prices, and economic indicators from various sources for market analysis, predictive modeling, or algorithmic trading.
What’s really Datascraping ?
Datascraping is a rapid method for extracting information from a computer-program-generated, human-readable source. It serves as an interface to access data without an API, swiftly extracting and locally storing relevant information. This technique proves valuable when specific data is required from online sources without API access, offering an efficient way for automated data collection.
There are several types of data scraping :
- Screen scraping :
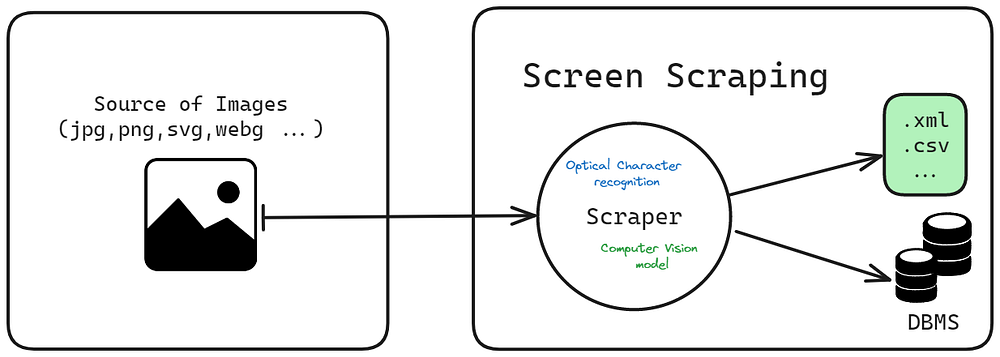
How Screen Scraping works
This is a technique where a computer program extracts data from the display output of another program. It’s often used to capture old screens and transfer the data to modern front-ends. Screen scraping is normally associated with the programmatic collection of visual data from a source, instead of parsing data as in web scraping.
Like Blackbox , it’s an extension that extracts code from videos, preserving indentation and allowing code selection from anywhere on the screen. It’s useful for developers watching coding tutorials.
- Report mining :
How Report Mining works
Report mining is a process that involves extracting and analyzing data from reports, typically in text file format. The goal is to transform the data from a static, unstructured format into a dynamic, structured format that can be easily understood and used for decision-making.
In the context of data mining, report mining can be seen as a specific application where the data to be mined is contained in reports. These reports could be in various formats such as PDFs, Word documents, or even web pages.
The extracted data can then be used for various purposes, such as identifying trends, making predictions, or informing strategic decisions. This makes report mining a valuable tool in fields like business intelligence, market research, and many others.
Like PBRS for Power BI that is a tool for scheduling your organization’s Power BI and SSRS Reports.
https://www.capterra.com/reporting-software/
- Webscraping :
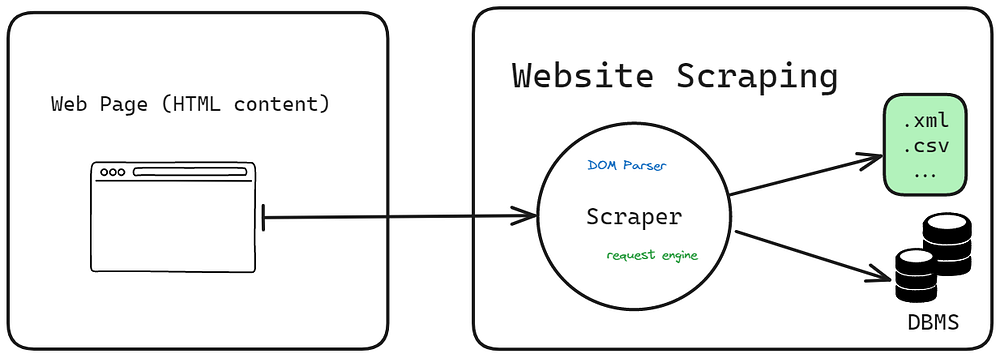
How Web Scraper works
Web scraping automates data extraction from websites using tools like DOM parsers. It involves retrieving text and media, This applies to various web page technologies, including JSP, Blade, JSX, etc, It’s possible to extract the data in HTTP or HTTPS and maybe also other protocols like FTP , The procedure of webscraping have 4 steps :
- Crawling :
Web crawling is the process of systematically and automatically browsing the internet, typically performed by a program or script known as a web crawler or spider. The main purpose of it is to gather information from various websites by navigating through their pages, following links, and extracting relevant data.
It’s a fundamental step in web scraping, which involves extracting specific information from websites for various purposes such as data analysis, research, or creating datasets. The collected data can include text, images, links, and other structured or unstructured information present on web pages.
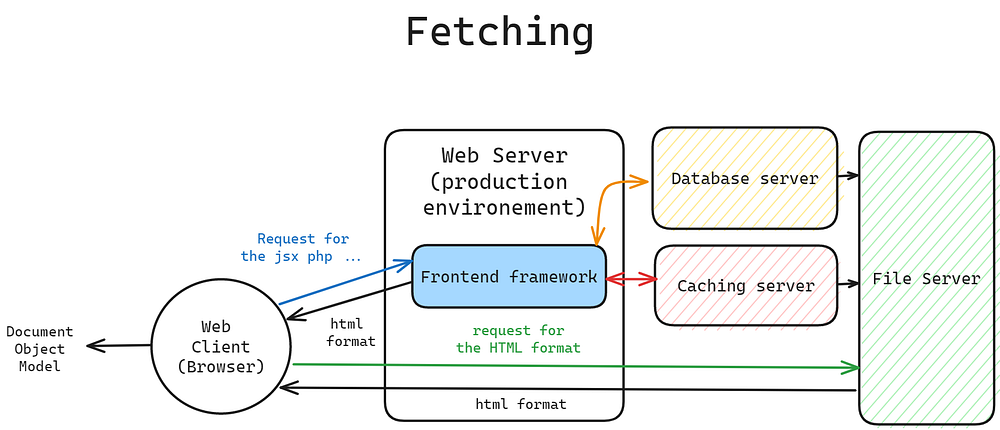
- Fetching :
Fetching refers to the process of obtaining additional data from a server, either on the server side using a programming language like Python or on the client side using JavaScript and AJAX, to update and enhance the content of a webpage without requiring a full page reload.
How web client fetch html for the DOM
Web frameworks on the server side generate HTML responses that are sent to the browser. The browser, in turn, parses the HTML to create a DOM tree, which represents the structure of the webpage. This DOM can be manipulated using JavaScript or Frontend Framworks, providing dynamic and interactive user experiences on the client side.
- Parsing :
Parsing in the context of web development refers to the process of analyzing a markup language, such as HTML or XML, and converting it into a structured representation that can be easily manipulated by a program. In Python, one popular library for parsing HTML is BeautifulSoup (bs4).
How parsing is done in the DOM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bs
u = 'https://example.com'
r = requests.get(u)
if r.status_code == 200:
soup = bs(r.content, 'html.parser')
t = soup.find('h1').text
print(f"Title: {t}")
links = soup.find_all('a')
for link in links:
print(f"Link: {link['href']} - Text: {link.text}")
else:
print(f"Failed. Status Code: {r.status_code}")
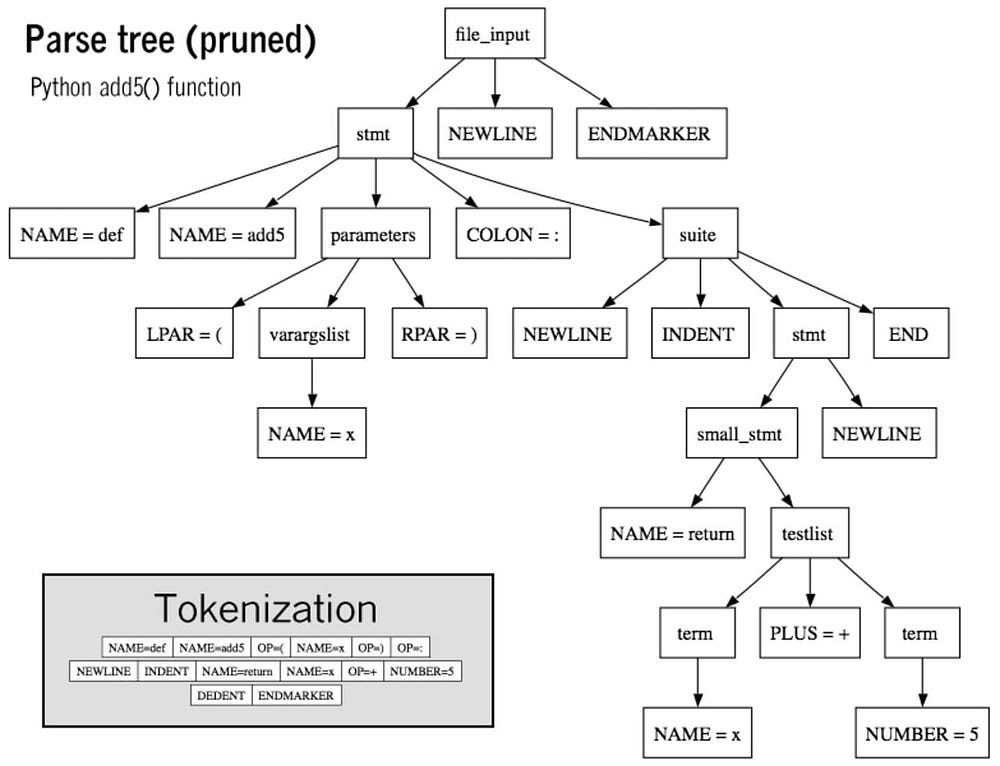
This is an example of Parse tree
How Parse Tree (pruned) is used to retreive data for python add5 method
- Storage :
It involves saving the parsed data in a structured manner for future use or reference.
For example once data is fetched and parsed, it might need to be stored for various purposes. In web development, this could involve saving user preferences, caching data for faster retrieval, or persisting data in databases for long-term storage. Storage mechanisms can include local storage, session storage, databases (SQL or NoSQL), or file systems.
Watch out web scraping is not always legal ?
Web scraping is a complex issue when it comes to legality , While the aim can be just to programmatically collect data for analysis or research. , Ethical and legal concerns arise when scraping is done without proper consent or violates a site’s terms of service.
To prevent issues like website overload or legal problems, ethical and lawful web scraping practices are crucial, ensuring compliance with permissions and site terms.
How to deal with webscraping ?
The legality of web scraping depends on various factors, including the website’s terms of service, the nature of the data being scraped, and the jurisdiction.
Generally, web scraping is legal when:
- Website Rules: Check the website’s rules or use its API if allowed for scraping Respect the website owner’s preferences by following the guidelines in the “robots.txt” file.
- Public Data: If data is public and no security measures are bypassed, it might be legal.
- Rate Limiting: Even if a website allows scraping, it may have rate limits to prevent overload. Respecting these limits is crucial to avoid being blocked.
- Data Usage: How the scraped data is used can also impact legality. For example, using scraped data for commercial purposes could be more likely to result in legal issues.
- Geographical Location: Laws vary by location. What’s legal in one country might not be in another.
- Consent: In some cases, explicit consent may be required to scrape personal data, especially under data protection regulations like GDPR.
Conversely, web scraping may be illegal if it involves:
- Don’t access private or password-protected parts of a website without permission; it’s usually illegal.
- If web scraping goes against a website’s rules (terms of service), it could be considered illegal.
- Scraping copyrighted content without permission can get you into legal trouble.
Otherwise , when encountering web scraping challenges, consider these steps:
- Use a fake useragent string with a UserAgent to potentially bypass connection rejections, although success isn’t guaranteed.
- Address issues where extracted HTML appears blank by incorporating a delay, such as using
time.sleep(), to ensure the complete loading of the page before scraping. - Adjust the scraping pace to prevent server overload and potential blocking, implementing time delays between requests.
If server blocks persist, explore Ip rotating as a potential solution to mitigate continuous blocking issues.
Thanks for reading my article , make sure to understand well the Legal issue of webscraping